
Health equity, the principle of ensuring everyone has a fair and just opportunity to be healthy, is a critical goal in today’s society. Achieving this goal requires addressing the root causes of health disparities, which often stem from social determinants of health.
Education and awareness programs play a vital role in dismantling these barriers and empowering individuals to make informed choices that lead to better health outcomes.
This article explores the profound impact of education and awareness programs in promoting health equity. We will delve into the concept of health equity, highlighting its differences from health equality and exploring the social factors that contribute to health disparities.
We will then examine how education empowers individuals to take control of their health, and how awareness campaigns can effectively target marginalized communities to address specific health concerns.
Defining Health Equity
Health equity is a fundamental principle that emphasizes the right of all individuals to achieve their optimal health, regardless of their social, economic, or other circumstances. It’s about ensuring everyone has a fair and just opportunity to be healthy, free from the limitations imposed by social, economic, and environmental factors.
Health Equity vs. Health Equality
Health equity is not the same as health equality. Health equality implies providing everyone with the same resources and services, regardless of their needs. While this may seem fair on the surface, it often overlooks the unique challenges faced by certain groups, leading to disparities in health outcomes.
For instance, providing everyone with the same healthcare access doesn’t address the underlying social and economic factors that contribute to health disparities, such as poverty, lack of education, or limited access to healthy food.Health equity, on the other hand, goes beyond equal access to healthcare and recognizes the need for tailored interventions to address the specific needs of different groups.
It acknowledges that certain groups, like those living in poverty or belonging to minority communities, may face unique barriers to health and require additional support to achieve optimal health.
Health Disparities Across Socioeconomic Groups
Health disparities are preventable differences in health outcomes between different population groups. These disparities are often rooted in social and economic inequalities, resulting in some groups experiencing poorer health than others. Here are some examples of health disparities across socioeconomic groups:
- Life Expectancy:People living in poverty have a significantly lower life expectancy than those with higher incomes. For instance, a study by the National Center for Health Statistics found that the average life expectancy for people living in poverty is 75.7 years, compared to 80.7 years for those with higher incomes.
- Infant Mortality:The infant mortality rate is significantly higher among infants born to mothers with lower socioeconomic status. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the infant mortality rate for infants born to mothers with a high school education or less is 7.5 per 1,000 live births, compared to 4.2 per 1,000 live births for infants born to mothers with a college degree.
- Chronic Diseases:People living in poverty are more likely to suffer from chronic diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and cancer. These diseases are often linked to poor nutrition, lack of access to healthcare, and exposure to environmental hazards.
- Mental Health:Mental health disparities are also prevalent across socioeconomic groups. People living in poverty are more likely to experience depression, anxiety, and other mental health conditions. This is often attributed to stress related to poverty, unemployment, and lack of access to mental health services.
Social Determinants of Health
The social determinants of health (SDOH) are the conditions in which people are born, grow, live, work, and age that influence their health outcomes. These factors include:
- Economic Stability:Income, employment, and access to affordable housing all contribute to health outcomes. People living in poverty are more likely to experience food insecurity, lack access to healthcare, and live in unsafe neighborhoods, all of which negatively impact their health.
- Education:Education levels are strongly linked to health outcomes. People with higher levels of education tend to have better health habits, higher incomes, and greater access to healthcare.
- Social and Community Context:Social connections, community safety, and access to social support systems are crucial for health. People living in isolated or unsafe communities may experience higher levels of stress, which can lead to poor health outcomes.
- Healthcare Access and Quality:Access to affordable and quality healthcare is essential for good health. However, many people, particularly those living in poverty or in rural areas, lack access to adequate healthcare services.
- Neighborhood and Built Environment:The physical environment in which people live, work, and play also impacts their health. Access to safe and affordable housing, transportation, and healthy food options are all important factors that contribute to health equity.
The SDOH play a significant role in shaping health equity. By addressing these factors, we can create a more equitable society where everyone has a fair chance to achieve optimal health.
Role of Education in Health Equity
Education is a powerful tool that can help to improve health equity. By equipping individuals with the knowledge and skills they need to make informed health decisions, education can empower them to take control of their own health and well-being.
Empowering Individuals Through Education
Education plays a crucial role in promoting health equity by enabling individuals to make informed decisions about their health. When people have access to accurate information about health risks, prevention strategies, and available resources, they are better equipped to make choices that support their well-being.
For example, understanding the link between smoking and lung cancer can motivate individuals to quit smoking or avoid starting in the first place. Similarly, knowledge about the importance of regular physical activity and a balanced diet can encourage individuals to adopt healthier lifestyle habits.
Successful Educational Programs
Numerous educational programs have demonstrated success in improving health outcomes and reducing health disparities. For instance, the American Heart Association’s “Heart-Healthy Living” program provides education and resources to individuals at risk of heart disease, empowering them to adopt healthier lifestyle choices and manage their condition effectively.
Another example is the “Healthy People 2030” initiative, which aims to achieve health equity by focusing on eliminating health disparities across various population groups. This initiative includes educational components that aim to raise awareness about health disparities and promote access to quality healthcare services for all.
A Hypothetical Educational Program: Diabetes Prevention
Let’s consider a hypothetical educational program designed to prevent Type 2 diabetes among individuals at risk. This program would target individuals with a family history of diabetes, those who are overweight or obese, and those with prediabetes. The program would consist of several components:
- Information Sessions:Regular sessions would provide participants with in-depth knowledge about Type 2 diabetes, including its causes, risk factors, and complications.
- Lifestyle Modification Workshops:Interactive workshops would guide participants on how to adopt healthy lifestyle habits, such as regular physical activity, a balanced diet, and stress management techniques.
- Support Groups:Support groups would provide a safe space for participants to share their experiences, challenges, and successes, fostering a sense of community and encouragement.
- Access to Resources:The program would connect participants with local resources, such as nutritionists, fitness trainers, and healthcare providers, to provide ongoing support and guidance.
By providing participants with the knowledge, skills, and support they need to make positive lifestyle changes, this program would empower them to prevent Type 2 diabetes and improve their overall health.
Importance of Awareness Programs

Awareness programs play a crucial role in promoting health equity by empowering individuals with knowledge and encouraging them to take proactive steps towards improving their health. These programs aim to bridge the gap in health literacy, particularly for marginalized communities, and equip them with the tools to navigate the healthcare system effectively.
Targeting Marginalized Communities
Awareness campaigns can effectively address health inequities by tailoring their messages and delivery methods to reach marginalized communities. This involves understanding the unique challenges and barriers these communities face, such as limited access to healthcare, cultural beliefs, and language differences.
By using culturally sensitive language, collaborating with trusted community leaders, and utilizing accessible communication channels, awareness campaigns can effectively reach these groups and promote health equity.
Impact of Education and Awareness Programs
Education and awareness programs play a crucial role in promoting health equity by empowering individuals to make informed decisions about their health. These programs aim to bridge the gap in knowledge, access, and resources that often contribute to health disparities.
Assessing the impact of these programs requires a comprehensive approach that considers various factors, including program design, implementation, and evaluation.
Evaluating the Effectiveness of Education and Awareness Programs
Evaluating the effectiveness of education and awareness programs is essential to ensure they are achieving their intended goals. Key metrics used to assess program impact include:
- Changes in knowledge, attitudes, and behaviors:Measuring changes in participants’ understanding of health risks, protective factors, and healthy behaviors is crucial. This can be achieved through pre- and post-program surveys, focus groups, and interviews.
- Increased access to healthcare services:Programs can be evaluated based on their ability to increase utilization of preventive screenings, early detection services, and other essential healthcare services.
- Improved health outcomes:The ultimate goal of education and awareness programs is to improve health outcomes. This can be measured through reductions in disease incidence, mortality rates, and hospitalizations.
- Program reach and engagement:Assessing the number of individuals reached by the program, as well as their level of engagement and participation, is essential for understanding program effectiveness.
- Cost-effectiveness:Evaluating the cost of program implementation against the achieved health benefits is crucial for ensuring sustainability and resource allocation.
Comparing Program Approaches
Different program approaches can have varying impacts on health outcomes. It is essential to consider the target audience, the specific health issue addressed, and the program’s overall goals.
- Community-based programs:These programs are often tailored to the specific needs and cultural context of the target community. They involve community members in program design and implementation, leading to greater ownership and engagement. Studies have shown that community-based programs can be effective in promoting health equity by addressing social determinants of health and building trust within the community.
- School-based programs:These programs focus on educating children and adolescents about health risks, healthy behaviors, and disease prevention. Early interventions through school-based programs can have long-term impacts on health outcomes. For example, programs that teach children about healthy eating habits and physical activity can contribute to lower rates of obesity and chronic diseases in adulthood.
- Media campaigns:Public awareness campaigns through television, radio, and social media can reach large audiences and raise awareness about health issues. These campaigns can be particularly effective in addressing stigma and promoting positive health behaviors.
- Provider-led interventions:Healthcare providers play a crucial role in educating patients about their health conditions, treatment options, and preventive measures. Provider-led interventions can be effective in improving adherence to medication regimens, reducing preventable hospitalizations, and promoting healthy lifestyle choices.
Data Analysis for Program Improvement
Data analysis is essential for informing program improvements and ensuring their effectiveness. By analyzing data collected during program implementation, organizations can identify areas for improvement and optimize program design and delivery.
- Identifying program strengths and weaknesses:Data analysis can help identify which program components are most effective and which areas need improvement. For example, analyzing survey data can reveal participants’ perceptions of program content, delivery methods, and overall effectiveness.
- Tailoring programs to specific needs:Data can be used to tailor programs to the specific needs and characteristics of the target population. For example, analyzing demographic data can help identify disparities in access to healthcare services and develop programs that address these disparities.
- Monitoring program progress and impact:Regular data collection and analysis are essential for monitoring program progress and assessing its impact on health outcomes. This allows for timely adjustments to program strategies and ensures that resources are being allocated effectively.
- Disseminating findings and best practices:Sharing program evaluation findings with other organizations and stakeholders can promote the adoption of best practices and improve the effectiveness of health equity initiatives.
Health Wellness, Health Equity, and Health Essentials
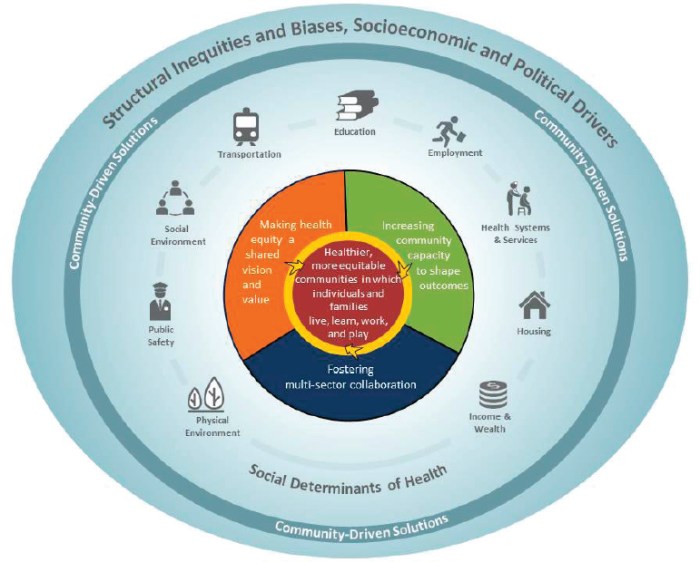
Health wellness, health equity, and health essentials are interconnected concepts that play a crucial role in achieving overall health improvement. Understanding the nuances of each concept and their relationship with one another is essential for developing effective strategies to promote health and well-being for all.
Understanding the Interconnections
These concepts are interconnected, forming a complex web that influences individual and community health outcomes.
- Health Wellness:This refers to an individual’s overall well-being, encompassing physical, mental, emotional, and social aspects. It involves making healthy choices, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress, and maintaining positive relationships. Health wellness is the foundation for achieving health equity.
- Health Equity:This focuses on ensuring that everyone has the opportunity to achieve their full health potential, regardless of their social, economic, or environmental circumstances. Health equity acknowledges that health disparities exist and aims to eliminate them through targeted interventions and policies.
- Health Essentials:These are the basic requirements for good health, such as access to safe and affordable housing, nutritious food, clean water, quality healthcare, and education. Health essentials provide the necessary resources for individuals to make healthy choices and maintain their well-being.
The Importance of Health Wellness, Health Equity, and Health Essentials
These concepts are crucial for achieving overall health improvement.
- Health Wellness:By promoting health wellness, individuals can take control of their health, reduce their risk of chronic diseases, and improve their quality of life.
- Health Equity:Addressing health disparities through health equity initiatives ensures that everyone has a fair chance at good health, regardless of their background. This leads to a healthier and more equitable society.
- Health Essentials:Access to health essentials empowers individuals to make healthy choices and access necessary healthcare services. This is essential for preventing disease, promoting early detection, and improving overall health outcomes.
Examples of Health Wellness Initiatives Contributing to Health Equity
Health wellness initiatives can contribute to achieving health equity in various ways.
- Community Health Centers:These centers provide affordable healthcare services to underserved communities, addressing disparities in access to healthcare.
- Nutrition Education Programs:Programs that educate individuals about healthy eating habits can help reduce disparities in food insecurity and improve overall health outcomes.
- Mental Health Awareness Campaigns:Raising awareness about mental health issues can reduce stigma and encourage individuals to seek help when needed, addressing disparities in mental health services.
Final Thoughts
By investing in education and awareness programs, we can create a more equitable healthcare system where everyone has the opportunity to thrive. These programs empower individuals to make informed choices, break down systemic barriers, and ultimately contribute to a healthier and more just society.
As we move forward, it’s essential to continue developing innovative and inclusive programs that meet the diverse needs of communities, ensuring that health equity is not just a goal, but a reality for all.
Answers to Common Questions
What are some examples of successful education programs that have improved health outcomes?
One notable example is the “Diabetes Prevention Program” developed by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). This program utilizes lifestyle modifications, such as weight loss and increased physical activity, to prevent or delay the onset of type 2 diabetes.
It has proven to be highly effective in reducing the risk of developing the disease.
How can awareness campaigns address health inequities by targeting marginalized communities?
Awareness campaigns can effectively address health inequities by tailoring their messages and outreach strategies to specific communities. For instance, a campaign focused on reducing smoking rates in low-income neighborhoods might utilize culturally relevant messaging and community partnerships to ensure that the information reaches the intended audience.
By understanding the unique needs and challenges of marginalized communities, awareness campaigns can be more impactful and effective.
What are some key metrics for evaluating the effectiveness of education and awareness programs?
Key metrics for evaluating program effectiveness include changes in knowledge, attitudes, and behaviors related to the health issue in question. For example, an education program aimed at increasing awareness of HIV prevention could be evaluated by measuring changes in participants’ knowledge about transmission routes, access to testing services, and use of protective measures.





